The tfds.features.FeatureConnector API:
- Defines the structure, shapes, dtypes of the final
tf.data.Dataset - Abstract away serialization to/from disk.
- Expose additional metadata (e.g. label names, audio sample rate,...)
Overview
tfds.features.FeatureConnector defines the dataset features structure (in
tfds.core.DatasetInfo):
tfds.core.DatasetInfo(
features=tfds.features.FeaturesDict({
'image': tfds.features.Image(shape=(28, 28, 1), doc='Grayscale image'),
'label': tfds.features.ClassLabel(
names=['no', 'yes'],
doc=tfds.features.Documentation(
desc='Whether this is a picture of a cat',
value_range='yes or no'
),
),
'metadata': {
'id': tf.int64,
'timestamp': tfds.features.Scalar(
tf.int64,
doc='Timestamp when this picture was taken as seconds since epoch'),
'language': tf.string,
},
}),
)
Features can be documented by either using just a textual description
(doc='description') or by using tfds.features.Documentation directly to
provide a more detailed feature description.
Features can be:
- Scalar values:
tf.bool,tf.string,tf.float32,... When you want to document the feature, you can also usetfds.features.Scalar(tf.int64, doc='description'). tfds.features.Audio,tfds.features.Video,... (see the list of available features)- Nested
dictof features:{'metadata': {'image': Image(), 'description': tf.string} },... - Nested
tfds.features.Sequence:Sequence({'image': ..., 'id': ...}),Sequence(Sequence(tf.int64)),...
During generation, the examples will be automatically serialized by
FeatureConnector.encode_example into a format suitable to disk (currently
tf.train.Example protocol buffers):
yield {
'image': '/path/to/img0.png', # `np.array`, file bytes,... also accepted
'label': 'yes', # int (0-num_classes) also accepted
'metadata': {
'id': 43,
'language': 'en',
},
}
When reading the dataset (e.g. with tfds.load), the data is automtically
decoded with FeatureConnector.decode_example. The returned tf.data.Dataset
will match the dict structure defined in tfds.core.DatasetInfo:
ds = tfds.load(...)
ds.element_spec == {
'image': tf.TensorSpec(shape=(28, 28, 1), tf.uint8),
'label': tf.TensorSpec(shape=(), tf.int64),
'metadata': {
'id': tf.TensorSpec(shape=(), tf.int64),
'language': tf.TensorSpec(shape=(), tf.string),
},
}
Serialize/deserialize to proto
TFDS expose a low-level API to serialize/deserialize examples to
tf.train.Example proto.
To serialize dict[np.ndarray | Path | str | ...] to proto bytes, use
features.serialize_example:
with tf.io.TFRecordWriter('path/to/file.tfrecord') as writer:
for ex in all_exs:
ex_bytes = features.serialize_example(data)
f.write(ex_bytes)
To deserialize to proto bytes to tf.Tensor, use
features.deserialize_example:
ds = tf.data.TFRecordDataset('path/to/file.tfrecord')
ds = ds.map(features.deserialize_example)
Access metadata
See the introduction doc to access features metadata (label names, shape, dtype,...). Example:
ds, info = tfds.load(..., with_info=True)
info.features['label'].names # ['cat', 'dog', ...]
info.features['label'].str2int('cat') # 0
Create your own tfds.features.FeatureConnector
If you believe a feature is missing from the available features, please open a new issue.
To create your own feature connector, you need to inherit from
tfds.features.FeatureConnector and implement the abstract methods.
- If your feature is a single tensor value, it's best to inherit from
tfds.features.Tensorand usesuper()when needed. Seetfds.features.BBoxFeaturesource code for an example. - If your feature is a container of multiple tensors, it's best to inherit
from
tfds.features.FeaturesDictand use thesuper()to automatically encode sub-connectors.
The tfds.features.FeatureConnector object abstracts away how the feature is
encoded on disk from how it is presented to the user. Below is a diagram showing
the abstraction layers of the dataset and the transformation from the raw
dataset files to the tf.data.Dataset object.
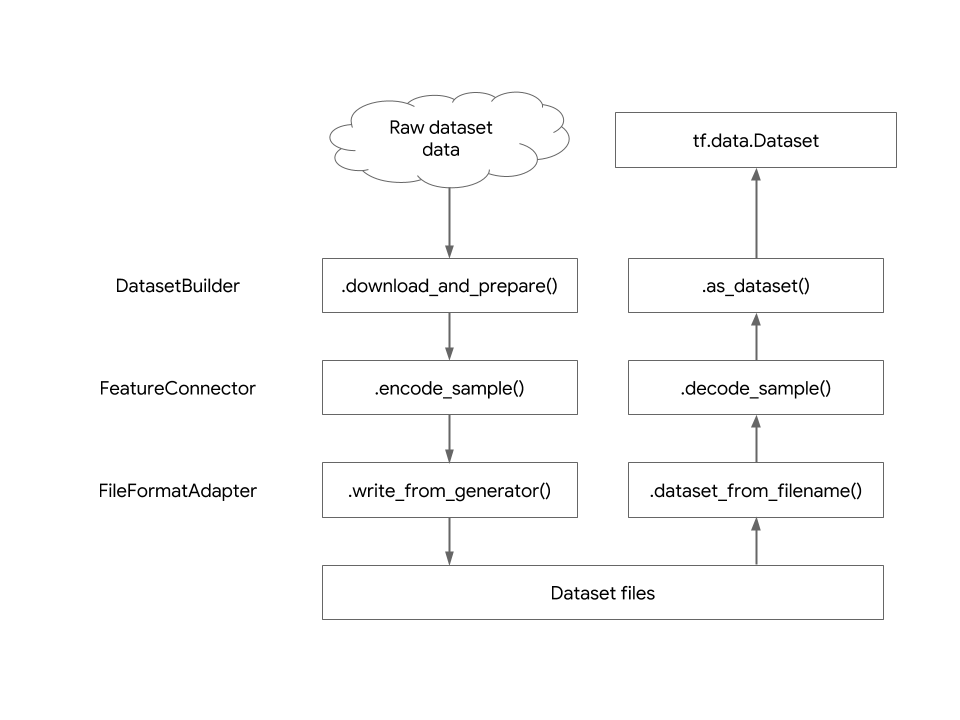
To create your own feature connector, subclass tfds.features.FeatureConnector
and implement the abstract methods:
encode_example(data): Defines how to encode the data given in the generator_generate_examples()into atf.train.Examplecompatible data. Can return a single value, or adictof values.decode_example(data): Defines how to decode the data from the tensor read fromtf.train.Exampleinto user tensor returned bytf.data.Dataset.get_tensor_info(): Indicates the shape/dtype of the tensor(s) returned bytf.data.Dataset. May be optional if inheriting from anothertfds.features.- (optionally)
get_serialized_info(): If the info returned byget_tensor_info()is different from how the data are actually written on disk, then you need to overwriteget_serialized_info()to match the specs of thetf.train.Example to_json_content/from_json_content: This is required to allow your dataset to be loaded without the original source code. See Audio feature for an example.
For more info, have a look at tfds.features.FeatureConnector documentation.
It's also best to look at
real examples.
